Acute Cholecystitis Treatment in Singapore – Symptoms, Risks & Surgery Options
What is Perforated Cholecystitis?
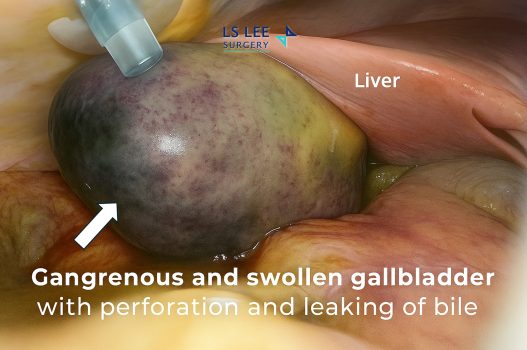
Perforated cholecystitis is a life-threatening complication of untreated or delayed acute cholecystitis. It occurs when the gallbladder becomes severely inflamed and swollen, cutting off its blood supply. This leads to gangrene (tissue death), followed by rupture (perforation) of the gallbladder wall.
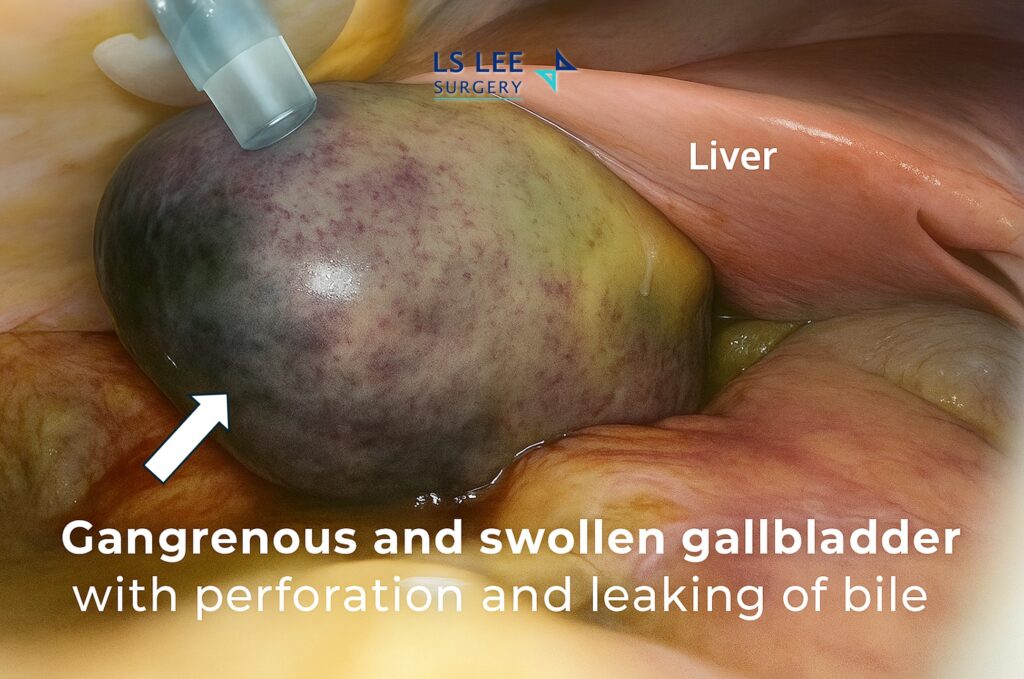
When the gallbladder bursts, bile and infected fluid leak into the abdominal cavity, causing widespread inflammation and infection. This condition requires urgent medical and surgical intervention.
Complications of Perforated Cholecystitis
If left untreated, bile leakage can result in severe complications such as:
- Bile peritonitis (infection of the abdominal lining)
- Liver or pelvic abscess formation
- Sepsis or septic shock
- Pneumonia from systemic infection
- Acute kidney failure due to overwhelming infection
Prompt diagnosis and aggressive treatment are essential to reduce the risk of death or long-term damage.
Symptoms of Perforated Gallbladder
- Severe pain in the right upper abdomen
- Pain may become generalized if bile spreads throughout the abdomen
- High fever and chills
- Rapid heart rate
- Nausea, vomiting
- Signs of shock (low blood pressure, confusion, weakness)
These symptoms may rapidly progress and should be treated as a surgical emergency.
Diagnosis of Perforated Cholecystitis
A CT scan of the abdomen is the most reliable imaging method to confirm the diagnosis. It helps detect:
- Gallbladder wall rupture
- Fluid collection in the abdomen
- Surrounding organ involvement
Blood tests will also show signs of infection, inflammation, and possible organ dysfunction.
Treatment for Perforated Cholecystitis
Treatment depends on the patient’s condition and the severity of the infection:
Emergency Surgery – Laparotomy
In most cases, an open surgical procedure (laparotomy) is required to:
- Remove the gallbladder
- Clean and drain the abdominal cavity
- Remove pus or bile collections
Standard laparoscopic cholecystectomy is typically not sufficient due to the extent of contamination.
Non-Surgical Management (for High-Risk Patients)
Patients who are unfit for immediate surgery due to sepsis, shock, or underlying conditions may initially be treated with:
- Intravenous antibiotics
- Percutaneous drainage to remove abscess or bile collection
Once stabilized, they may undergo delayed gallbladder removal.
Why Immediate Treatment Matters
Perforated cholecystitis carries a high risk of mortality if not treated promptly. Early diagnosis and surgical intervention significantly improve survival and reduce complications.
When to Seek Emergency Care
If you experience any of the following symptoms, seek immediate medical attention:
- Severe or spreading abdominal pain
- High fever and chills
- Jaundice
- Fainting or confusion
- Signs of shock