Acute Cholecystitis Treatment in Singapore – Symptoms, Risks & Surgery Options
What is Acute Cholecystitis?
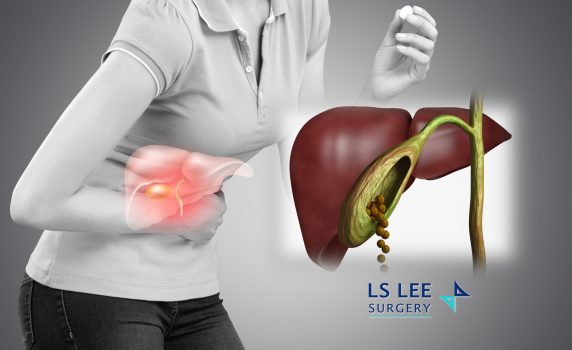
Acute cholecystitis is a sudden and severe inflammation of the gallbladder. It commonly presents as intense, constant pain in the right upper abdomen, often accompanied by fever, nausea, and vomiting. This condition occurs when a gallstone becomes lodged in the neck of the gallbladder, blocking bile flow.
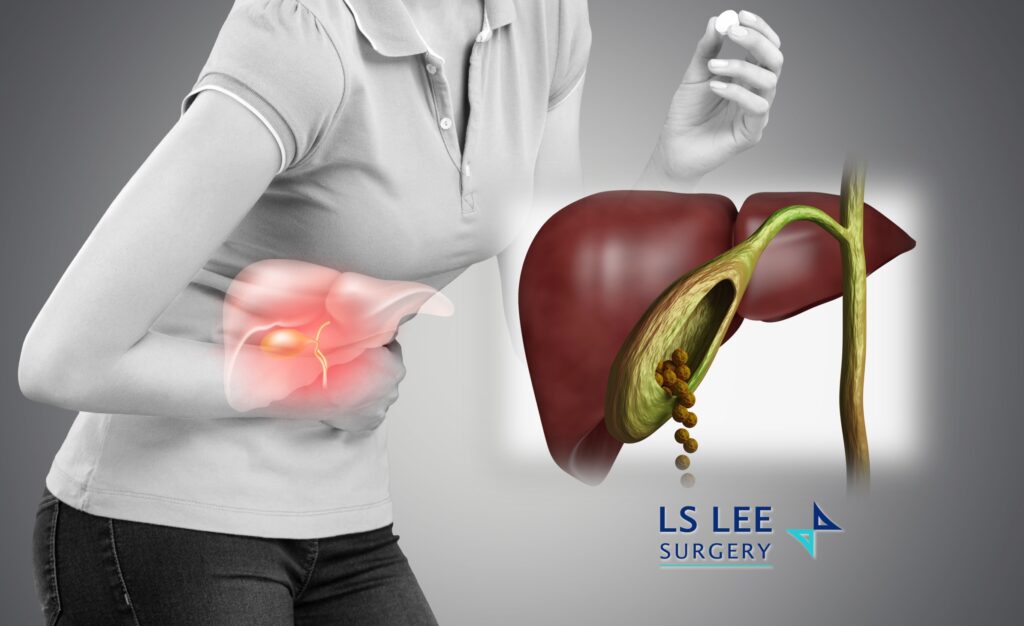
When bile is trapped inside the gallbladder, it becomes stagnant and prone to bacterial infection. If left untreated, acute cholecystitis can lead to serious complications such as:
- Gangrenous cholecystitis (tissue death)
- Perforated gallbladder (rupture)
- Sepsis (life-threatening infection)
- Liver abscess
Prompt medical treatment is crucial.
Common Symptoms of Acute Cholecystitis
- Persistent pain in the upper right abdomen (may radiate to the back or right shoulder)
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal tenderness or bloating
- Loss of appetite
These symptoms typically appear suddenly and do not subside without medical intervention.
Diagnosis of Acute Cholecystitis
To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor will perform the following:
- Blood tests to detect signs of infection or inflammation (elevated white blood cells, liver enzymes)
- Abdominal ultrasound to check for gallstones, gallbladder wall thickening, or fluid
- CT scan or MRI if the ultrasound is inconclusive or complications are suspected
Treatment Options for Acute Cholecystitis
Initial Medical Management:
- Fasting to rest the digestive system
- IV fluids to prevent dehydration
- Pain relief with medications
- IV antibiotics to treat infection
Definitive Treatment – Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
Once stabilized, most patients will require laparoscopic gallbladder removal (cholecystectomy):
- Performed via keyhole surgery
- Minimally invasive with shorter recovery time
- Prevents recurrence and further complications
- Recommended within 24–72 hours of diagnosis, if suitable
Gallbladder Drainage (Percutaneous Cholecystostomy)
For patients who are not fit for surgery, a tube may be placed into the gallbladder to drain infected bile and relieve pressure.
Complications of Delayed Treatment
Without timely treatment, acute cholecystitis can escalate to:
- Gallbladder rupture
- Infection spreading to the liver or bloodstream
- Long-term digestive problems
This condition should be considered a medical emergency.
Prevention of Acute Cholecystitis
Although it’s not always preventable, you can reduce the risk by managing gallstones early. Individuals with known gallstones and symptoms such as biliary colic should consult a specialist to consider gallbladder removal before complications develop.
When to See a Gallbladder Specialist (HPB Surgeon)
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Sudden, severe right upper abdominal pain
- Pain that lasts more than a few hours
- Fever or jaundice
Prompt treatment can prevent serious complications and improve outcomes.